 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Splicing factor PTBP1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis via oncogenic splice-switching of MAPT
1 Guangzhou Institute of Cancer Research, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510095, China
2 Medical Oncology, Yuebei People Hospital, Shaoguan, 512026, China
* Corresponding Authors: GUOPING ZHANG. Email: ; MIN DENG. Email:
# Wenying Zheng and Yanyan Shang contributed equally to this work
Oncology Research 2025, 33(5), 1121-1133. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.060958
Received 13 November 2024; Accepted 04 March 2025; Issue published 18 April 2025
Abstract
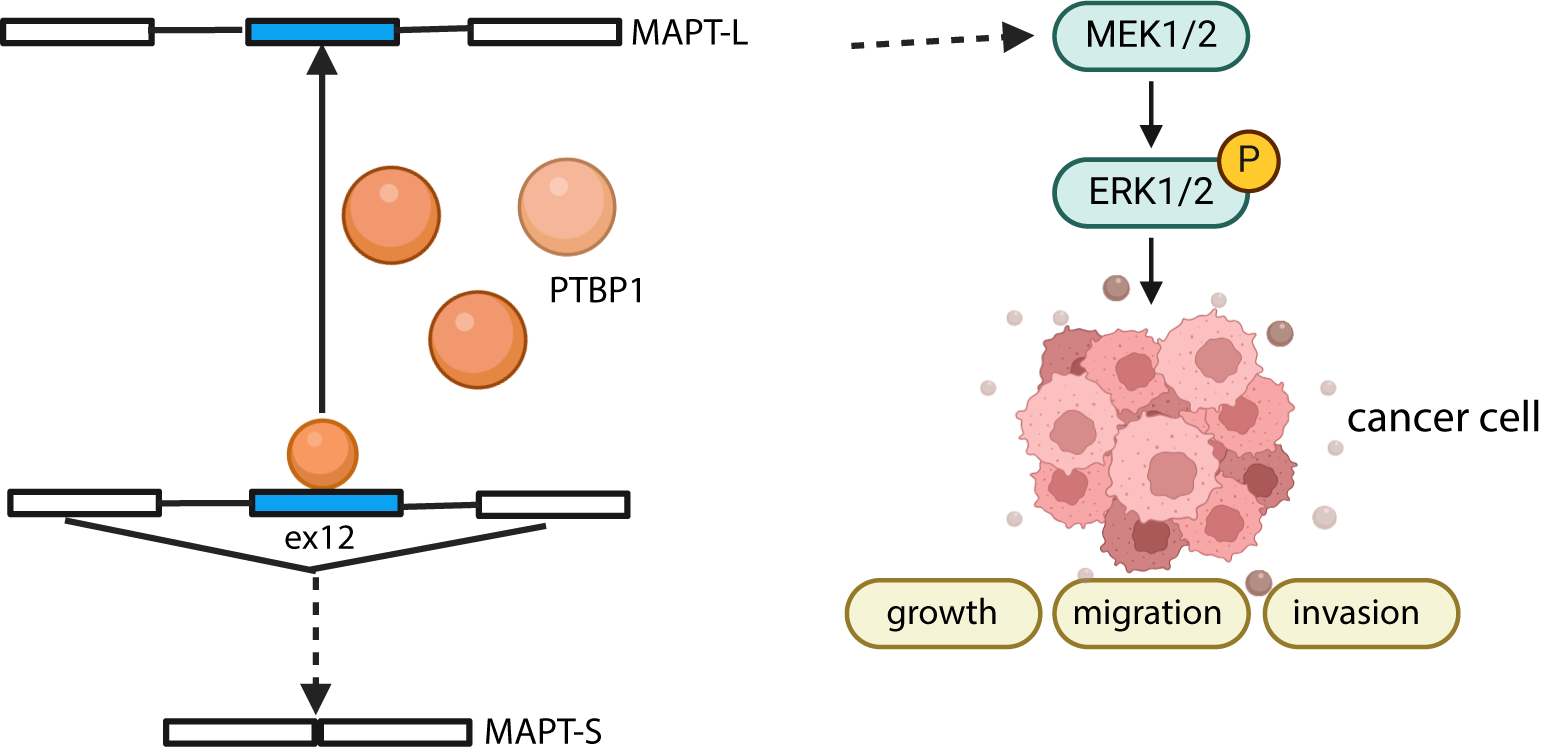
Background: Alterations in splicing factors contribute to aberrant alternative splicing (AS), which subsequently promotes tumor progression. The splicing factor polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) has been shown to facilitate cancer progression by modulating oncogenic variants. However, its specific role and underlying mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain to be elucidated. Methods: PTBP1 expression was evaluated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Subsequently, cells were transfected with vectors designed for PTBP1 overexpression or downregulation. The biological function of PTBP1 was assessed in vitro and in vivo using MTS assays, colony formation assays, transwell assays, xenograft formation, tail vein injection, and orthotopic models. Transcriptome analysis was conducted to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Results: Our findings demonstrated that PTBP1 exhibited elevated expression in HCC cell lines and tissues. Furthermore, its expression positively correlated with overall and disease-free survival rates, as well as tumor grade and stage. PTBP1 knockdown reduced HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and suppressed hepatocarcinoma xenograft growth and infiltration in vivo. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) analysis identified the AS events associated with PTBP1. PTBP1 functionally enhanced cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by modulating the AS of the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) gene and promoting oncogene expression. Notably, the dysregulation of MAPT splicing coincided with increased PTBP1 expression in HCC. Conclusions: PTBP1-guided AS of the MAPT gene enhances tumorigenicity in HCC through activation of the MAPK/ERK pathways.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools