 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Study on the Improvement of Foaming Properties of PBAT/PLA Composites by the Collaboration of Nano-Fe3O4 Carbon Nanotubes
1 Key Laboratory of Bio-Based Material Science & Technology, Northeast Forestry University, Ministry of Education, Harbin, 150040, China
2 Northeast Forestry University Engineering Consulting and Design Research Institute Co., Ltd., Harbin, 150040, China
* Corresponding Authors: Ce Sun. Email: ; Yanhua Zhang. Email:
# These two authors contributed equally and should be considered as co-first authors
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(4), 669-685. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0042
Received 20 February 2025; Accepted 26 March 2025; Issue published 21 April 2025
Abstract
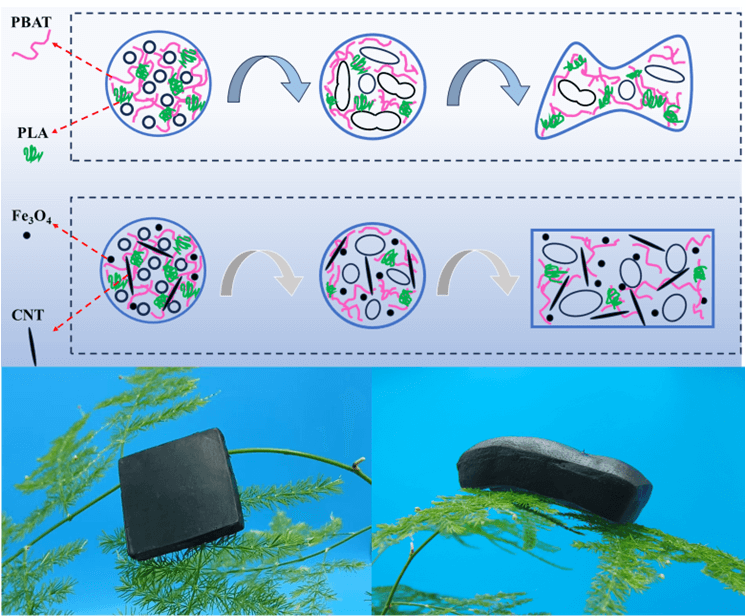
In recent years, degradable materials to replace petroleum-based materials in preparing high-performance foams have received much research attention. Degradable polymer foaming mostly uses supercritical fluids, especially carbon dioxide (Sc-CO2). The main reason is that the foams obtained by Sc-CO2 foaming have excellent performance, and the foaming agent is green and pollution-free. In current research, Poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly (lactic acid) (PLA), and other degradable polymers are generally used as the main foaming materials, but the foaming performance of these degradable polyesters is poor and requires modification. In this work, 10% PLA was added to PBAT to enhance the melt strength and improve the foaming performance. To improve the foaming properties of the PBAT/PLA composites, two kinds of nano-filler (nano-Fe3O4 and carbon nanotubes (CNTs)) were innovatively introduced for foaming modification. There was a synergistic effect between the two nano-fillers to enhance the foaming properties significantly. When 6 wt% CNTs and 4 wt% nano-Fe3O4 were added, the 4Fe3O4/6CNT foam had the best comprehensive performance. Its foaming rate reached 14.8 times, which was 2.8 and 2.1 times that after adding 10 wt% CNTs or 10 wt% nano-Fe3O4 alone. The combined action could adjust the melt elasticity of different PBAT/PLA composites to the optimum. The nanofillers also served as skeleton structures to support the foam cells, significantly improving the foaming performance. The density and foaming ratio did not change significantly at 14 days after foaming. The compressive strength of the composite foam reached up to 0.27 MPa and the water contact angle reached 120.1°. The synergistic foaming effect of nano-Fe3O4 and CNTs could significantly improve the Sc-CO2 foaming performances of the composites, providing a new method for degradable materials to replace petroleum-based materials.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools