 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Renewable Energy-Based Solutions for Decentralized Electrification: Demand Assessment and Multi-Tier Framework Approach
1 ACE-ESD/College of Science & Technology, University of Rwanda, Kigali, 4285, Rwanda
2 School of Engineering, University of Eldoret, Eldoret, 30100, Kenya
3 College of Education, University of Rwanda, Kigali, 4285, Rwanda
* Corresponding Author: Jacob Manyuon Deng. Email:
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(5), 1839-1862. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.063398
Received 14 January 2025; Accepted 20 March 2025; Issue published 25 April 2025
Abstract
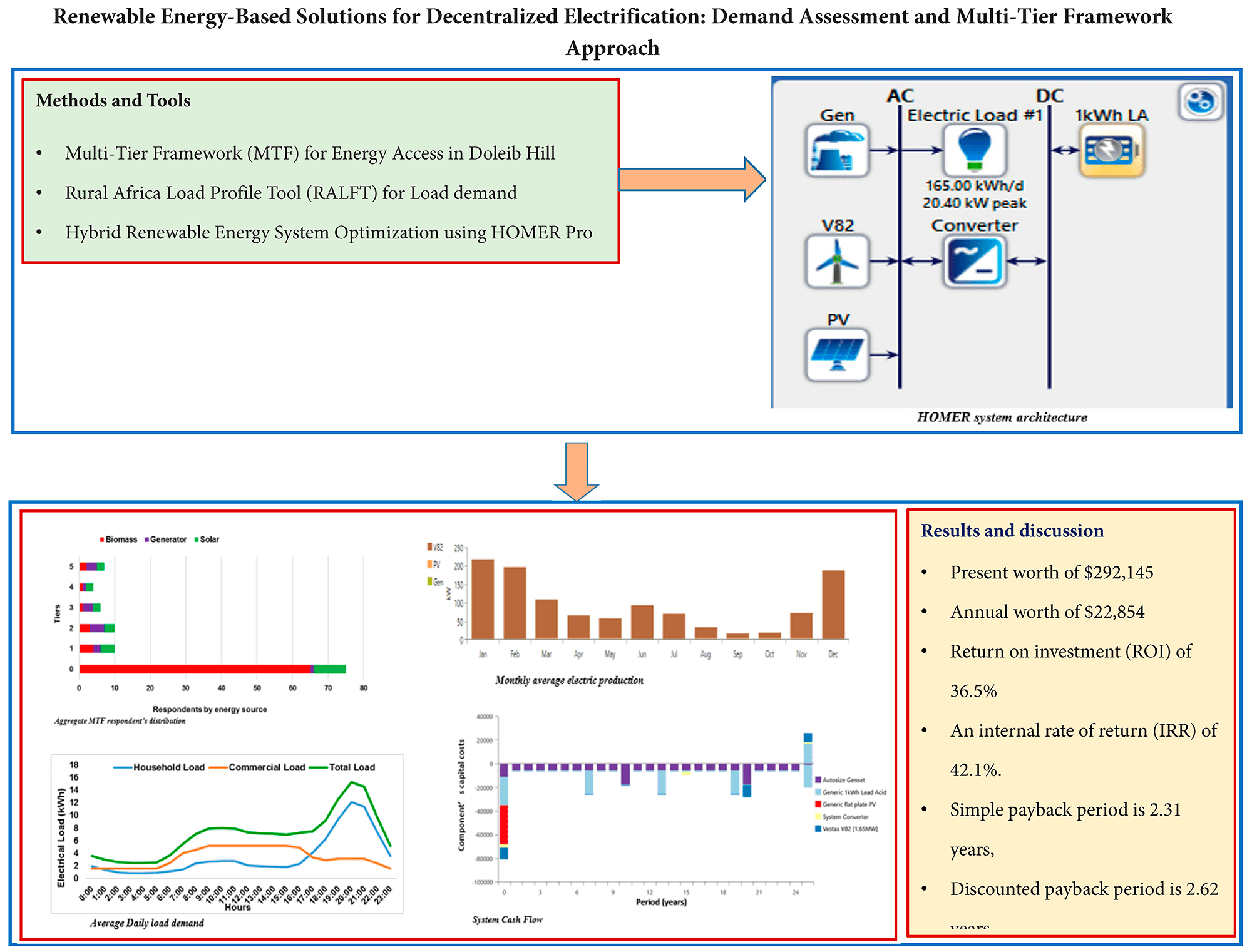
Energy access remains a critical challenge in rural South Sudan, with communities heavily relying on expensive and unfriendly environmental energy sources such as diesel generators and biomass. This study addresses the predicament by evaluating the feasibility of renewable energy-based decentralized electrification in the selected village of Doleib Hill, Upper Nile, South Sudan. Using a demand assessment and the Multi-Tier Framework (MTF) approach, it categorizes households, public facilities, private sector, Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and business energy needs and designs an optimized hybrid energy system incorporating solar Photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines, batteries, and a generator. The proposed system, simulated in Hybrid Optimization Model Electric Renewable (HOMER) Pro, demonstrates strong economic viability, with a present worth of $292,145, an annual worth of $22,854, a return on investment (ROI) of 36.5%, and an internal rate of return (IRR) of 42.1%. The simple payback period is 2.31 years, and the discounted payback period is 2.62 years. The system achieves a levelized cost of energy (LCOE) of $0.276/kWh and significantly reduces dependence on diesel, producing 798,800 kWh annually from wind energy. This research provides a replicable model for cost-effective, sustainable rural electrification, offering valuable insights for policymakers and energy planners seeking to expand electricity access in off-grid communities.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools