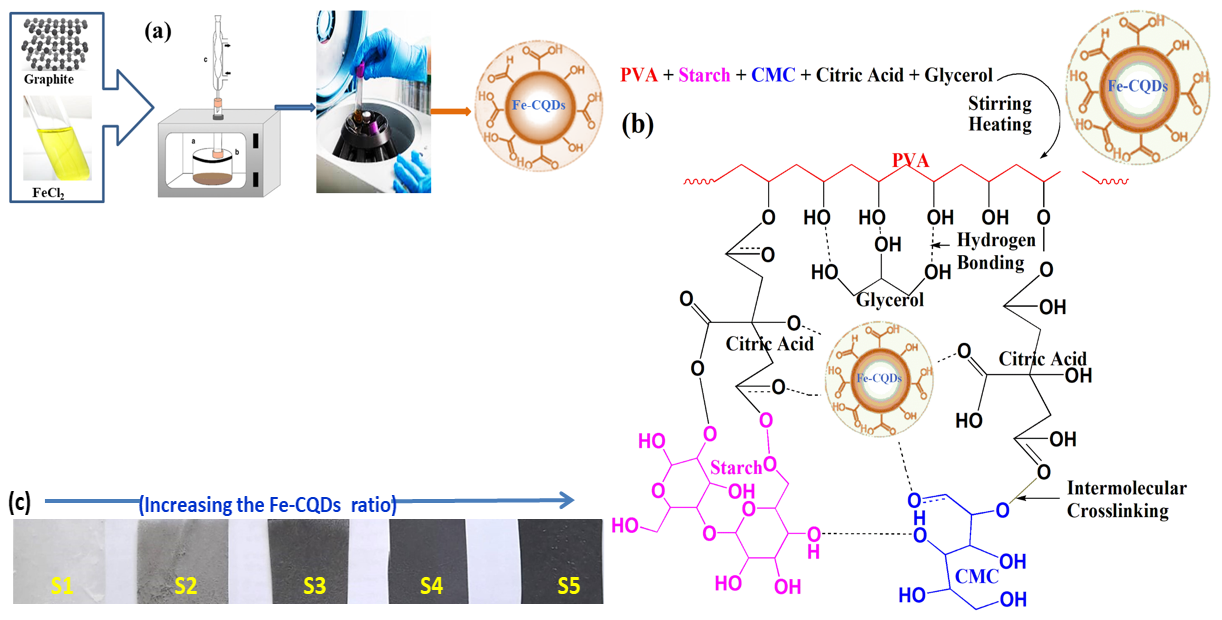
Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lekaa K. Abdul Karem1, Badriah Saad Al-Farhan2, Ghada M. G. Eldin3, Samir Kamel4, Ahmed M. Khalil5,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0046
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
Abstract In this study, the casting process is used to fabricate modified polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), starch (S), and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) polymer blend films (PVA/S/CMC) loaded with various concentrations of iron-doped carbon quantum dots (Fe-CQDs) and denoted as (PVA/S/CMC@Fe-CQDs). A one-step microwave strategy was employed as a facile method to prepare Fe-CQDs. Through a series of characterization techniques, fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, x-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) have been used to show the successful integration of Fe-CQDs into the PVA/S/CMC matrix. Loading the synthesized Fe-CQDs to the polymeric matrix significantly enhanced the… More >
Graphic Abstract
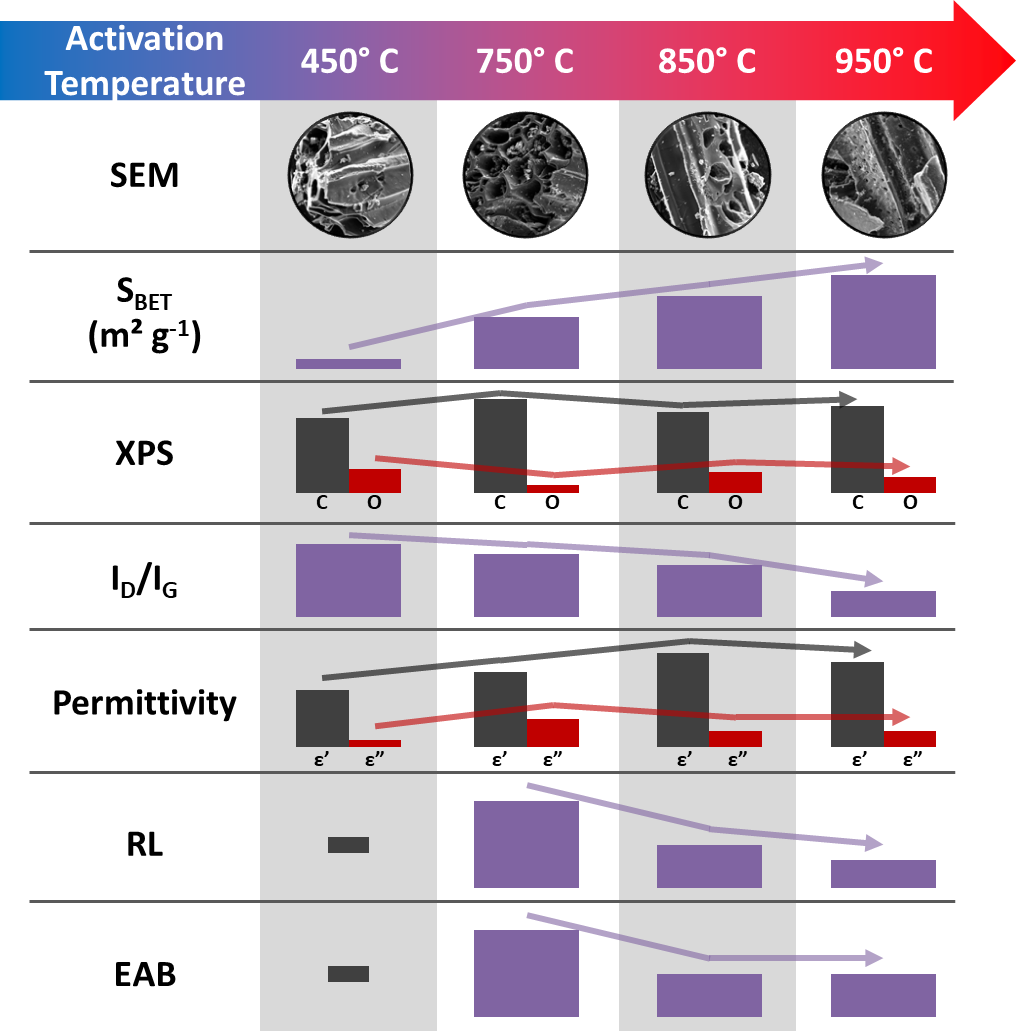
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nila Cecília Faria Lopes Medeiros1,2, Gisele Amaral-Labat1, Leonardo Iusuti de Medeiros1,2, Alan Fernando Ney Boss1, Beatriz Carvalho da Silva Fonseca1, Manuella Gobbo de Castro Munhoz3, Guilherme F. B. Lenz e Silva3, Mauricio Ribeiro Baldan1, Flavia Lega Braghiroli4,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0017
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Nanostructured Porous Materials: Synthesis, Processing, and Applications)
Abstract Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from the thermochemical conversion of biomass under oxygen-free conditions, has emerged as a sustainable resource for radar-absorbing technologies. This study explores the production of activated biochars from end-of-life wood panels using a scalable and sustainable physical activation method with CO2 at different temperatures, avoiding the extensive use of corrosive chemicals and complex procedures associated with chemical or vacuum activation. Compared to conventional chemically or vacuum-activated biochars, the physically activated biochar demonstrated competitive performance while minimizing environmental impact, operational complexity, and energy consumption. Furthermore, activation at 750°C reduces energy consumption by 14%… More >
Graphic Abstract
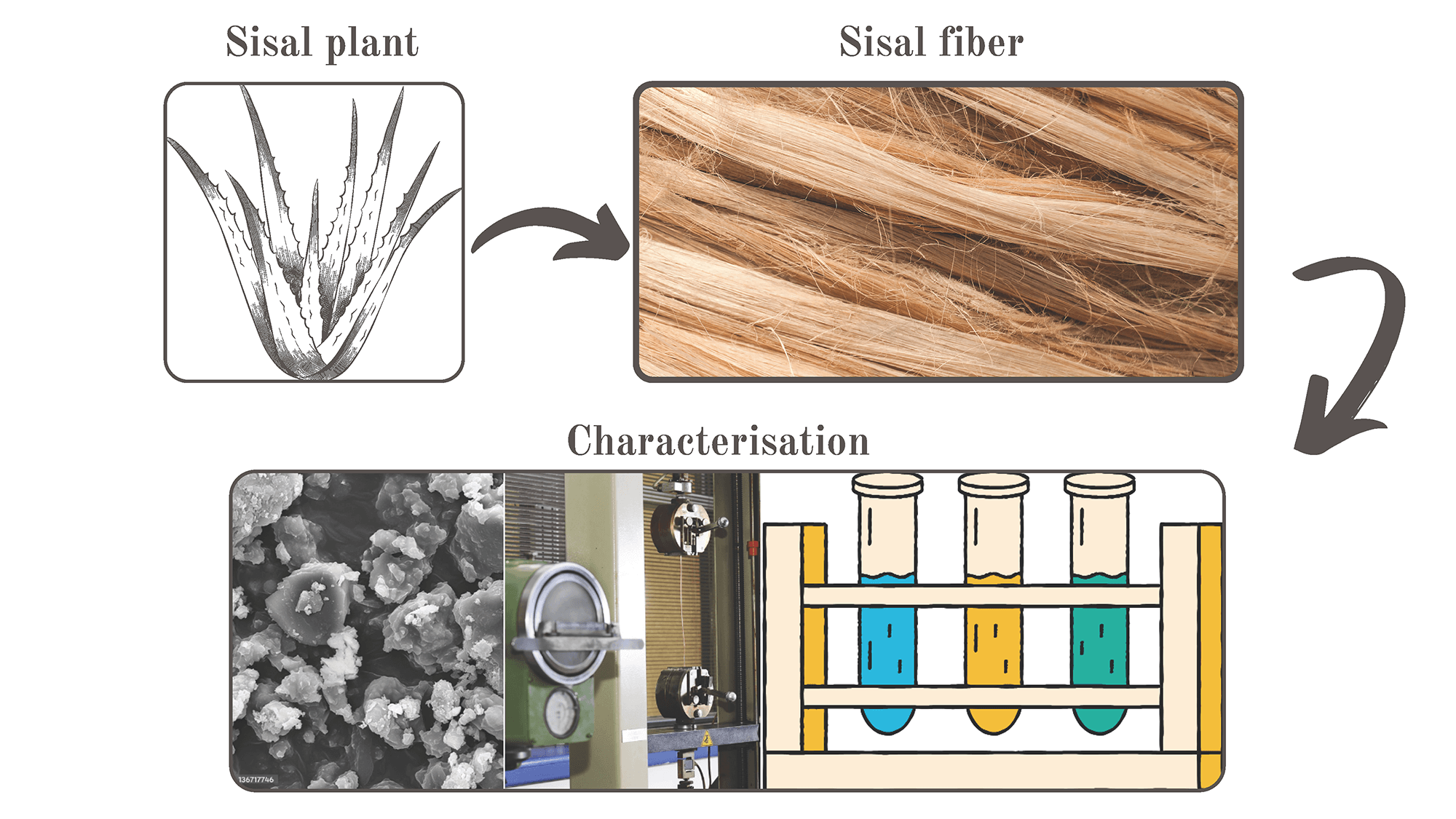
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Timothy K. Mulenga1,2, Albert U. Ude1, Vivekanandhan Chinnasamy1, Resego Phiri2, Sanjay Mavinkere Rangappa2,*, Suchart Siengchin2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0015
Abstract This study presents for the first time, the characterization of the physical, chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties of Botswana sisal fibers. The aim was to evaluate the characteristics of sisal fibers from Botswana as potential reinforcement materials. The fibers were harvested from the outskirts of Selebi Phikwe, Botswana, and extracted using the scraping method without surface treatment. The analysis techniques of X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis and scanning electron microscopy were employed to characterize the properties of the lignocellulosic fibers. The chemical composition revealed 69.5% cellulose, 15.7% hemicellulose, 9.5% lignin, 2.07% ash, 5.73% More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Duc Hoa Pham, Bijender Kumar, Samia Adil, Jaehwan Kim*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0040
Abstract Increasing bio-based content in composites without compromising performance is an urgent duty toward sustainability and carbon neutralization. This paper reports high bio-content thermoset resin and cellulose long filament (CLF)-reinforced green composite by using a semi-bio imine-based hardener. The hardener (VDDM) is synthesized from DDM grafted with vanillin, and a bio-based vanillyl alcohol epoxy (VAE) monomer is used to prepare highly bio-based thermoset resin. The VAE-VDDM thermoset shows high tensile strength and Young’s modulus up to 94.8 MPa and 2.69 GPa, respectively. Further, a natural fiber-reinforced green composite is made with CLF and the prepared VAE-VDDM More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hammadi El Farissi1,2,*, Anass Choukoud1,2, Bouchaib Manoun3,4, Mohamed El Massaoudi5,6, Abdelmonaem Talhaoui2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0004
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Biochar and Carbon-Based Materials Characteristics and Environment Applications)
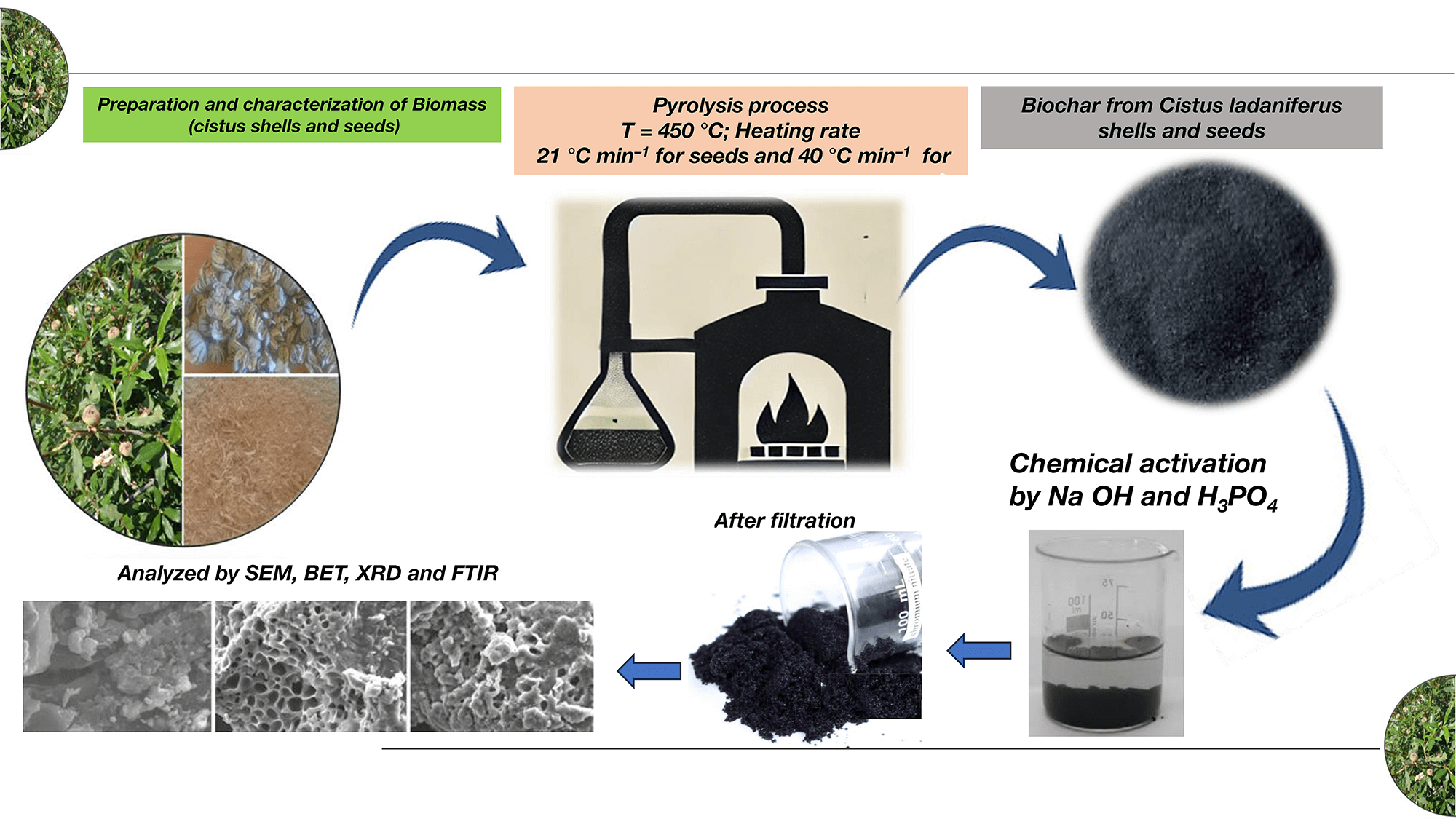
Abstract In light of the growing urgency to address environmental degradation and improve carbon sequestration strategies, this study rigorously investigates the potential of Cistus ladaniferus as a viable feedstock for biochar and activated carbon production. The influence of pyrolysis temperature, heating rate and particle size on biochar yield was systematically examined. The results demonstrate that increasing pyrolysis temperature and heating rate significantly reduces biochar yield, while particle size plays a crucial role in thermal degradation and biochar retention. To evaluate the structural and chemical properties of the materials, various characterization techniques were employed, including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Souha Mansour1,2,*, Amandine Viretto1,2, Marie-France Thevenon1,2,*, Loïc Brancheriau1,2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0078
Abstract The use of agricultural residues in biocomposite production has gained increasing attention, driven by several benefits. Converting agricultural by-products into bio-based materials within a circular economy represents a sustainable strategy to mitigate lignocellulosic waste, reduce reliance on fossil resources, and lower environmental pollution. This approach also creates economic opportunities for rural African communities by generating diverse income sources for workers in collection, processing, and manufacturing. As a result, the integration of agricultural residues into biocomposites production not only addresses environmental concerns but also fosters economic growth and supports rural development. In this review, five biomasses… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Wohua He, Fangji Wu, Haoqun Hong*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0005
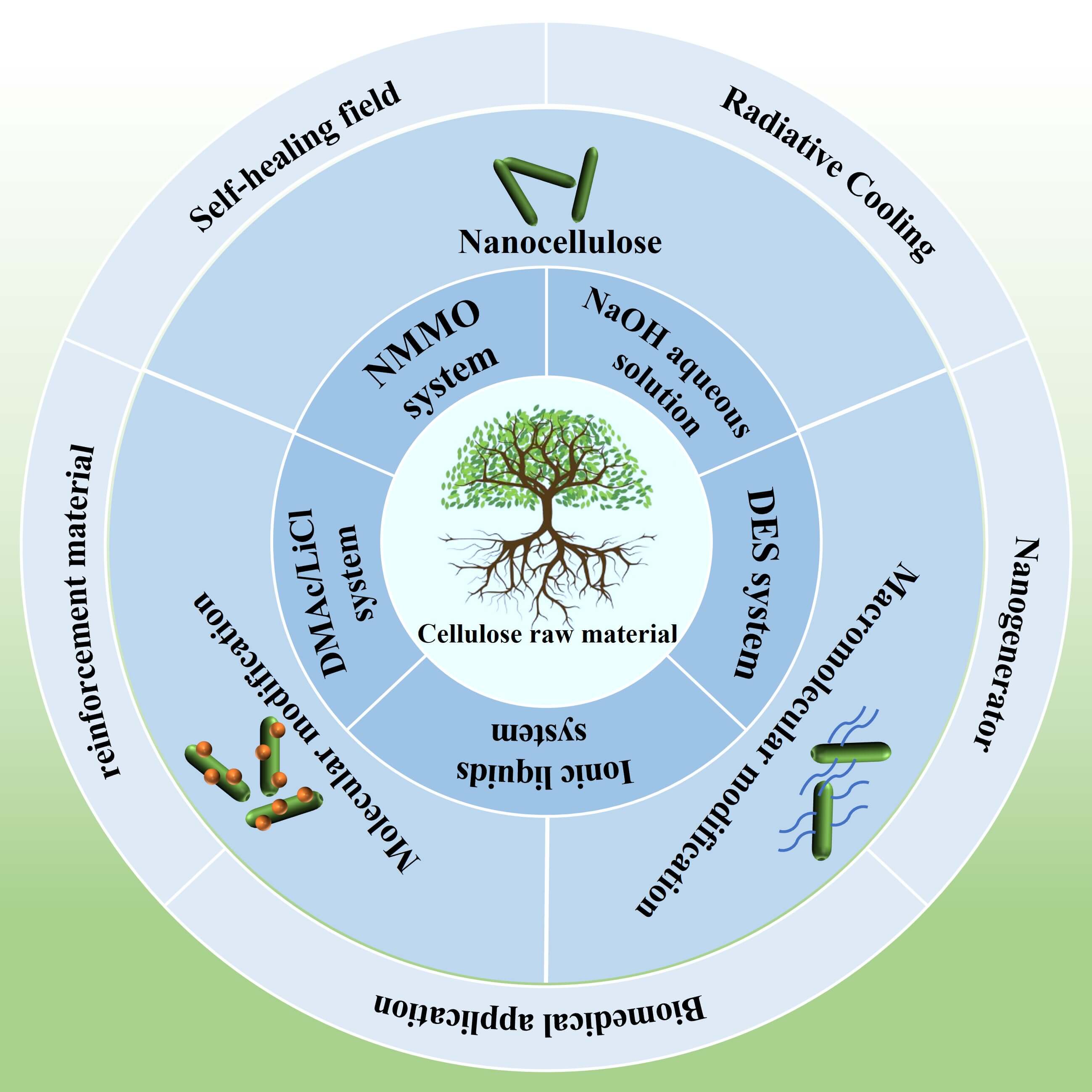
Abstract Under the background of the current energy crisis and environmental pollution, the development of green and sustainable materials has become particularly urgent. As one of the most abundant natural polymers on earth, cellulose has attracted wide attention due to its green recycling, sustainable development, degradability, and low cost. Therefore, cellulose and its derivatives were used as the starting point for comprehensive analysis. First, the basic structural properties of cellulose were discussed, and then the extraction and utilization methods of cellulose were reviewed, including Sodium Hydroxide based solvent system, N, N-Dimethylacetamide/Lithium Chloride System, N-Methylmorpholine-N-Oxide (NMMO) system, More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pelita Ningrum1, Sri Hidayati1,*, Wahyu Hidayat2, Samsul Rizal1, Erika Ayu Agustiany3, Emma Rochima4,5, Lee Seng Hua6, Antonio Di Martino7, Apri Heri Iswanto8, Widya Fatriasari3,5,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0006
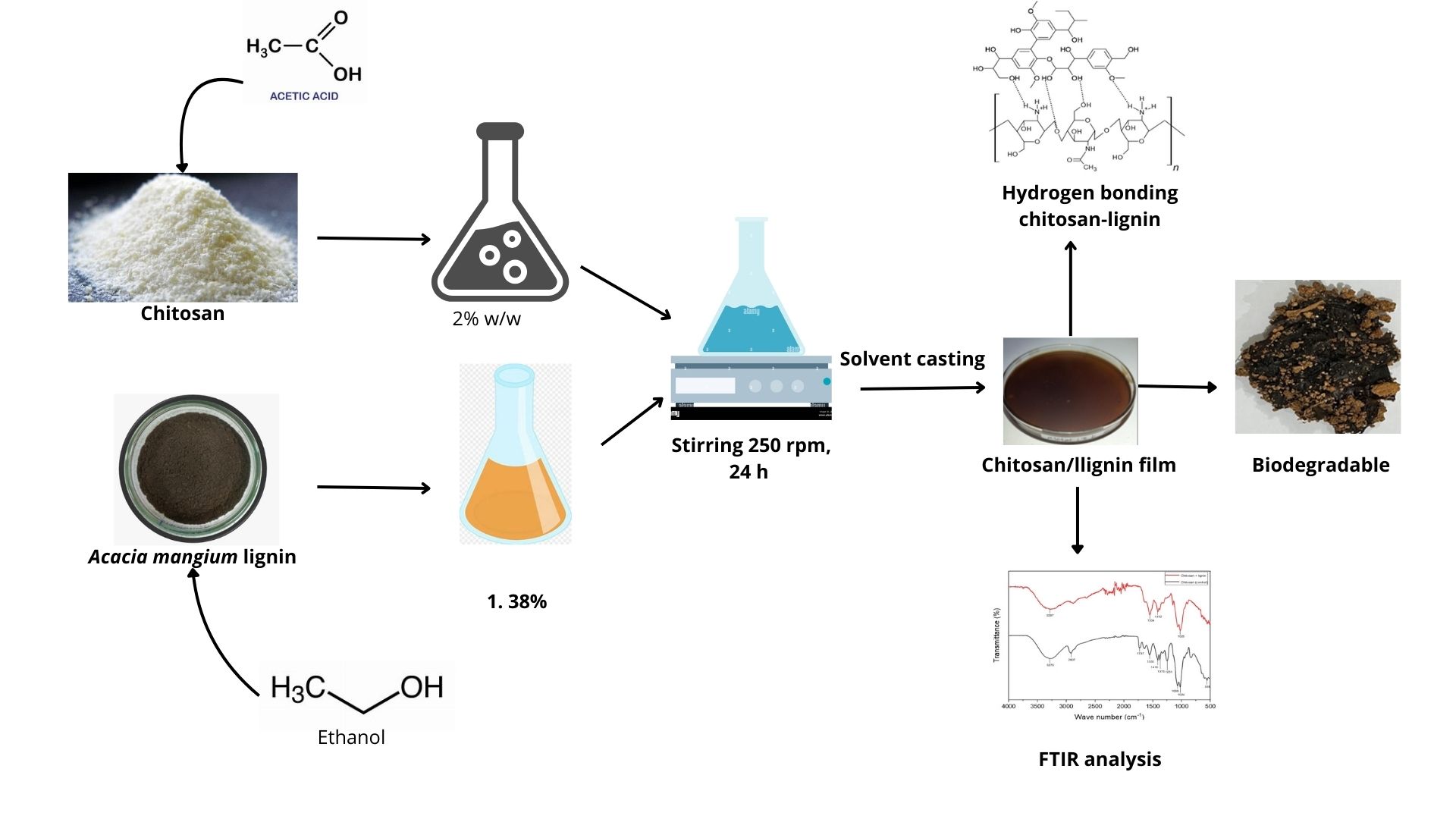
Abstract Biodegradable plastics are types of plastics that can decompose into water and carbon dioxide the actions of living organisms, mostly by bacteria. Generally, biodegradable plastics are obtained from renewable raw materials, microorganisms, petrochemicals, or a combination of all three. This study aims to develop an innovative bioplastic by combining chitosan and lignin. Bioplastic was prepared by casting method and characterized by measuring the mechanical properties like tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and elongation at break. The chemical structure, together with the interactions among chitosan and lignin and the presence of new chemical bonds, were evaluated by… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jun-Jie Yang1, Ran An1, Jing-Heng Nie1, Hao-Miao Ma1, Yu-Qing Yan1, Yuan-Ru Guo1,*, Qing-Jiang Pan2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0066
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biochar Based Materials for a Green Future)
Abstract To achieve the sustainable development and carbon neutral target, biomass chitosan (CS) was used to prepare N,S-doped biochar (NSB) with the assistance of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS). The synthetic route was developed, which does not require the activation that is frequently-used for active carbon materials. By manipulating their interaction, SDBS was deposited with CS in neutral and basic conditions. Subsequent calcination successfully has access to NSB. It features with hierarchical porous structure and abundant functional groups. The dually-doped NSB bears excellent adsorption performance towards chlortetracycline (CTC). The adsorption capacity reaches 101.3 mg g−1 within 4 More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhenzhou Wang1, Rui Luo1, Wenqing Yang1, Seng Hua Lee2,*, Wei Chen Lum3, Longjiang Liu4, Xiaojian Zhou1, Jun Zhang1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0073
Abstract Highly flame-retardant bio-based composites were prepared in this study. Firstly, glucose-citric acid (GC) resin was synthesized through the interaction of glucose and citric acid derived from agricultural and forestry sources. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) served as a toughening agent, whereas walnut shell powder (WSP) functioned as a filler in the formulation of a thermosetting bio-based GC-PVA-WSP (GCPW) composite with GC resin. The findings demonstrated that boric acid increased the limited oxygen index (LOI) value of GCPW to 33%, while simultaneously diminishing its total smoke production (TSP) by 99.9%, and achieving a flame retardant index (FRI) of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Nasmi Herlina Sari1,*, Suteja1, Widya Fatriasari2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0058
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Valorization of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Functional Materials)
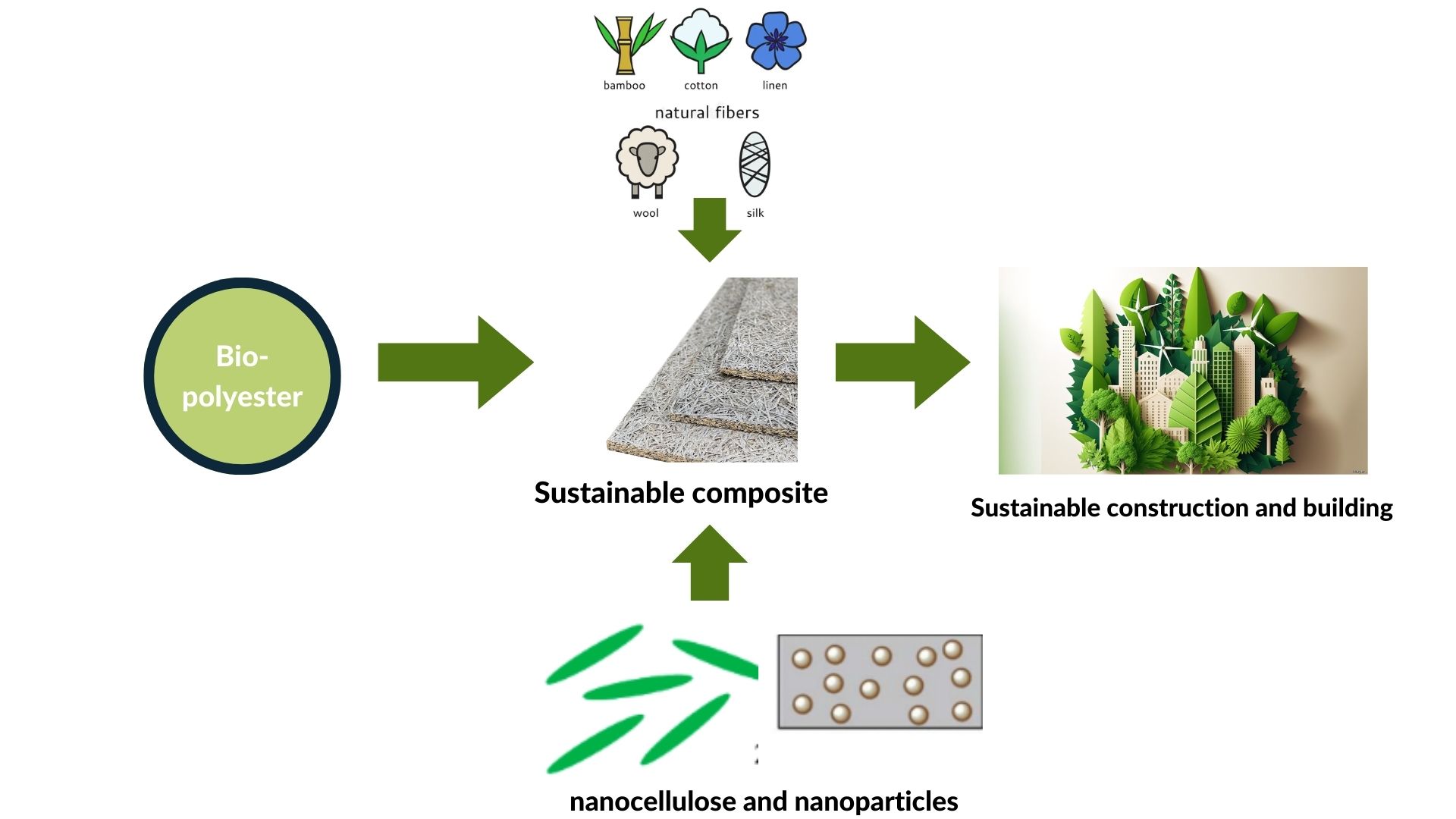
Abstract Composites made from biopolymers and natural fibers are gaining popularity as alternative sustainable structural materials. Biopolyesters including polylactic acid (PLA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), when mixed with natural fibers such as kenaf, hemp, and jute, provide an environmentally acceptable alternative to traditional fossil-based materials. This article examines current research on developments in the integration of biopolymers with natural fibers, with a focus on enhancing mechanical, thermal, and sustainability. Innovative approaches to surface treatment of natural fibers, such as biological and chemical treatments, have demonstrated enhanced adhesion with biopolymer matrices, increasing attributes such as… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Belkis Sulbarán-Rangel1,*, Jorge Armando Caldera Siller1, Salvador García Enríquez2, José Anzaldo-Hernandez2, Jenny Arratia-Quijada3, Marianelly Esquivel Alfaro4
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0061
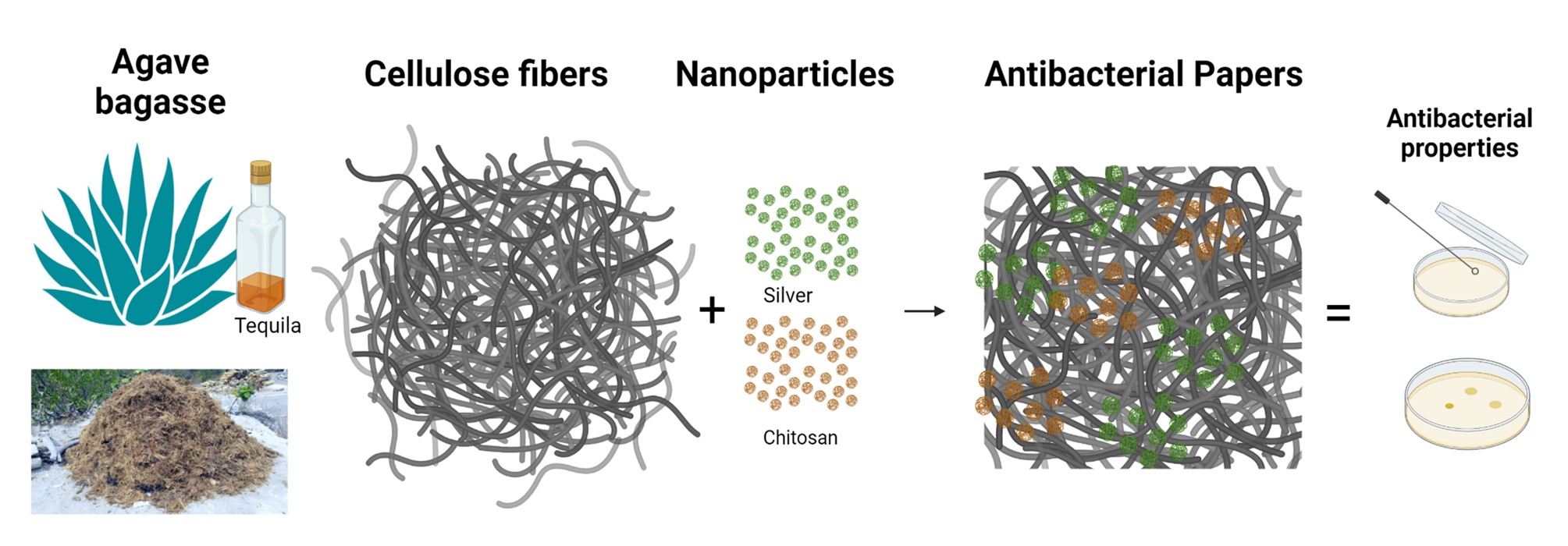
Abstract In this research, the antibacterial properties of a composite material prepared from agave bagasse cellulose fibers doped with silver nanoparticles and chitosan were studied. The development of composite materials with antibacterial properties and environmentally friendly based on cellulose fibers from agave bagasse with silver nanoparticles prepared by green synthesis and chitosan from shrimp waste enhances the value of these agro-industrial wastes and offers the opportunity for them to have biomedical applications since these raw materials have been poorly reported for this application. The antibacterial properties of chitosan and silver nanoparticles are already known. However, the… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zihan Ma1,2, Yan Wu1, Hongyan Wang2,*, Shaofei Yuan2, Jian Zhang2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0040
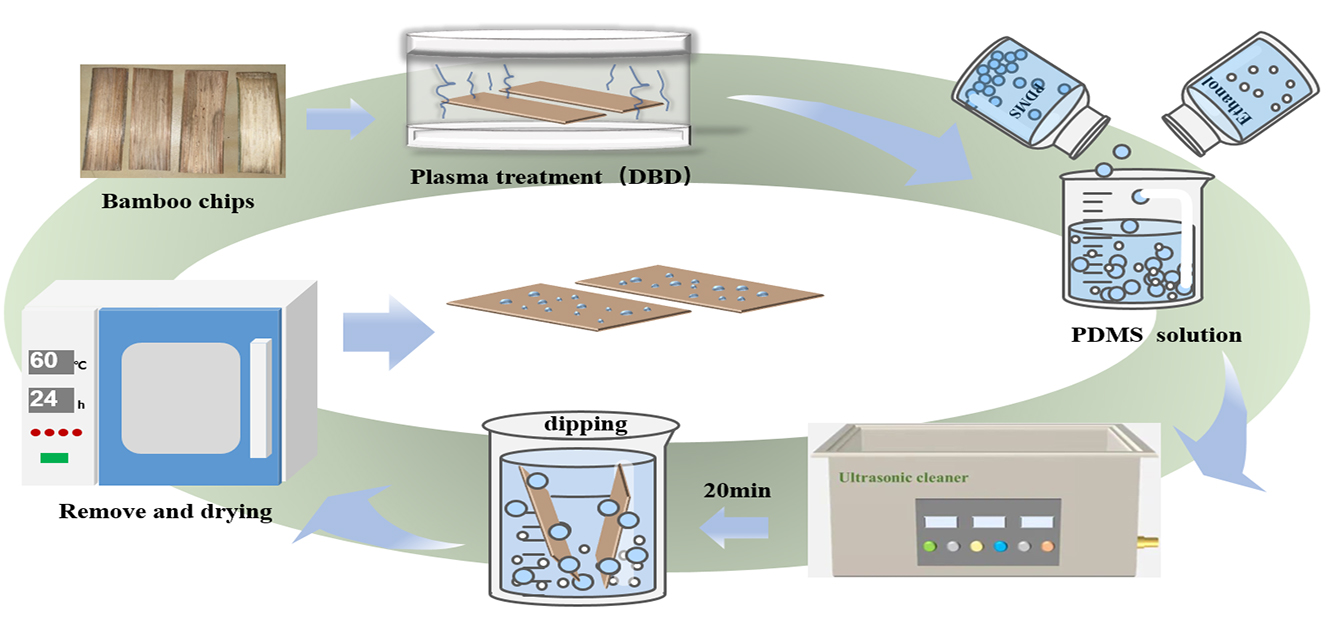
Abstract Herein, the surface of Moso bamboo was hydrophobically modified by combining O2/N2 plasma treatments with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) solution treatment as the hydrophobic solution. The effects of plasma treatment process (power and time), PDMS solution concentration, and maceration time on the hydrophobic performance of bamboo specimens were studied, and the optimal treatment conditions for improving the hydrophobicity were determined. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to analyze the surface morphology, chemical structure, and functional groups in the specimens before and after the plasma and PDMS… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tongtong Wang1,#, Zhenhui Pan2,#, Di Zhang2, Hui Shi1,2,*, Murat Yılmaz3, Amit Kumar4, Gaurav Sharma4, Tao Liu2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0043
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Biochar and Carbon-Based Materials Characteristics and Environment Applications)
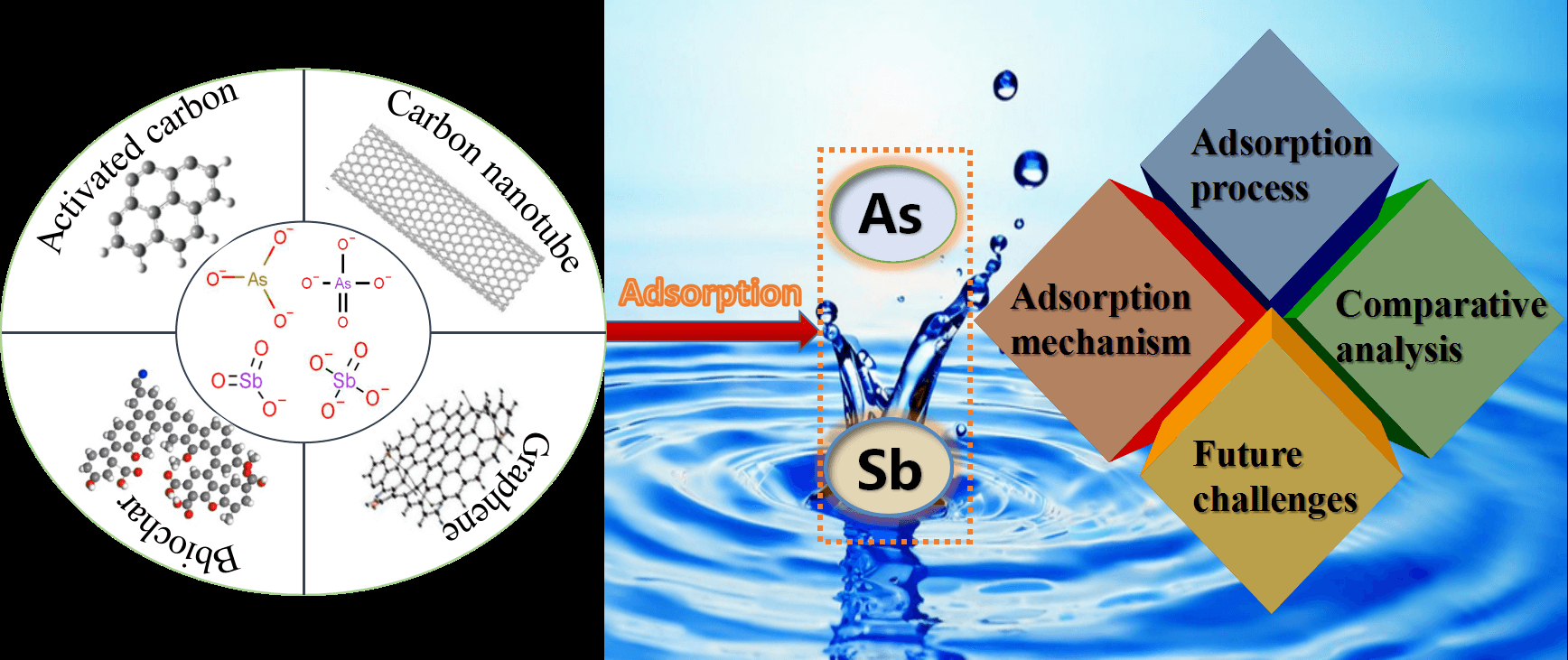
Abstract With the rapid development of industry, the environmental problems caused by heavy metal arsenic and antimony are becoming increasingly serious. Therefore, it is urgent to solve the problem of arsenic and antimony pollution in the water environment. Renewable carbon-based materials, as a kind of adsorbent widely used in wastewater treatment, have been the focus of scholars’ research for many years. In this review, the preparation methods, characteristics, and applications of renewable carbon-based materials (biochar, activated carbon, carbon nanotubes, and graphene) for the removal of arsenic and antimony are described in detail. Based on adsorption kinetics,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mariia Dmitrenko1, Daniel Pasquini2,*, Marcela Piassi Bernardo2, João Marcelo de Lima Alves2, Anna Kuzminova1, Ilnur Dzhakashov1, Andrey Terentyev3, Alexander Dyachkov3, K. S. Joshy4, Maya Jacob John5, Sabu T Tomas4, Anastasia Penkova1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0023
Abstract Petrochemical plastics are widely used for food protection and preservation; however, they exhibit poor
biodegradability, resisting natural degradation through physical, chemical, or enzymatic processes. As a sustainable
alternative to conventional plastic packaging, edible fflms offer effective barriers against moisture, gases, and microbial
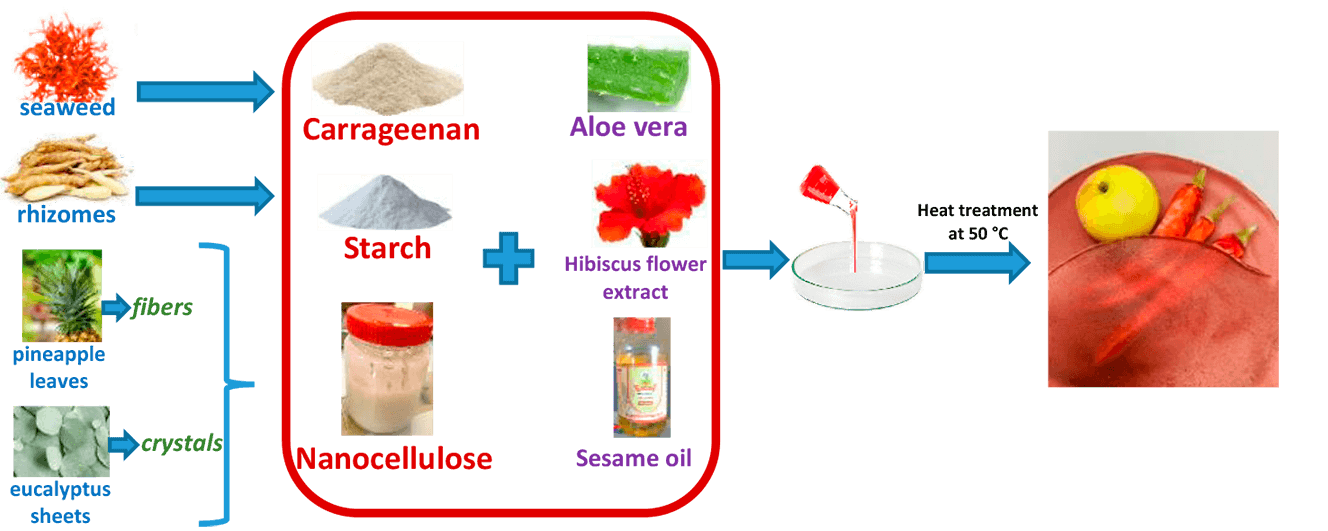
contamination while being biodegradable, biocompatible, and environmentally friendly. In this study, novel active food
packaging materials (in fflm form) were developed by incorporating starch, carrageenan, nanocellulose (NC), Aloe
vera, and hibiscus ffower extract. TTe effects of varying the matrix composition (26.5–73.5 wt.% starch/carrageenan),
NC concentration (2.77–17.07 wt.%), and particle type (ffbers or crystals)… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ega Cyntia Watumlawar1, Byung-Dae Park1,*, Long Yang2, Guanben Du2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0056
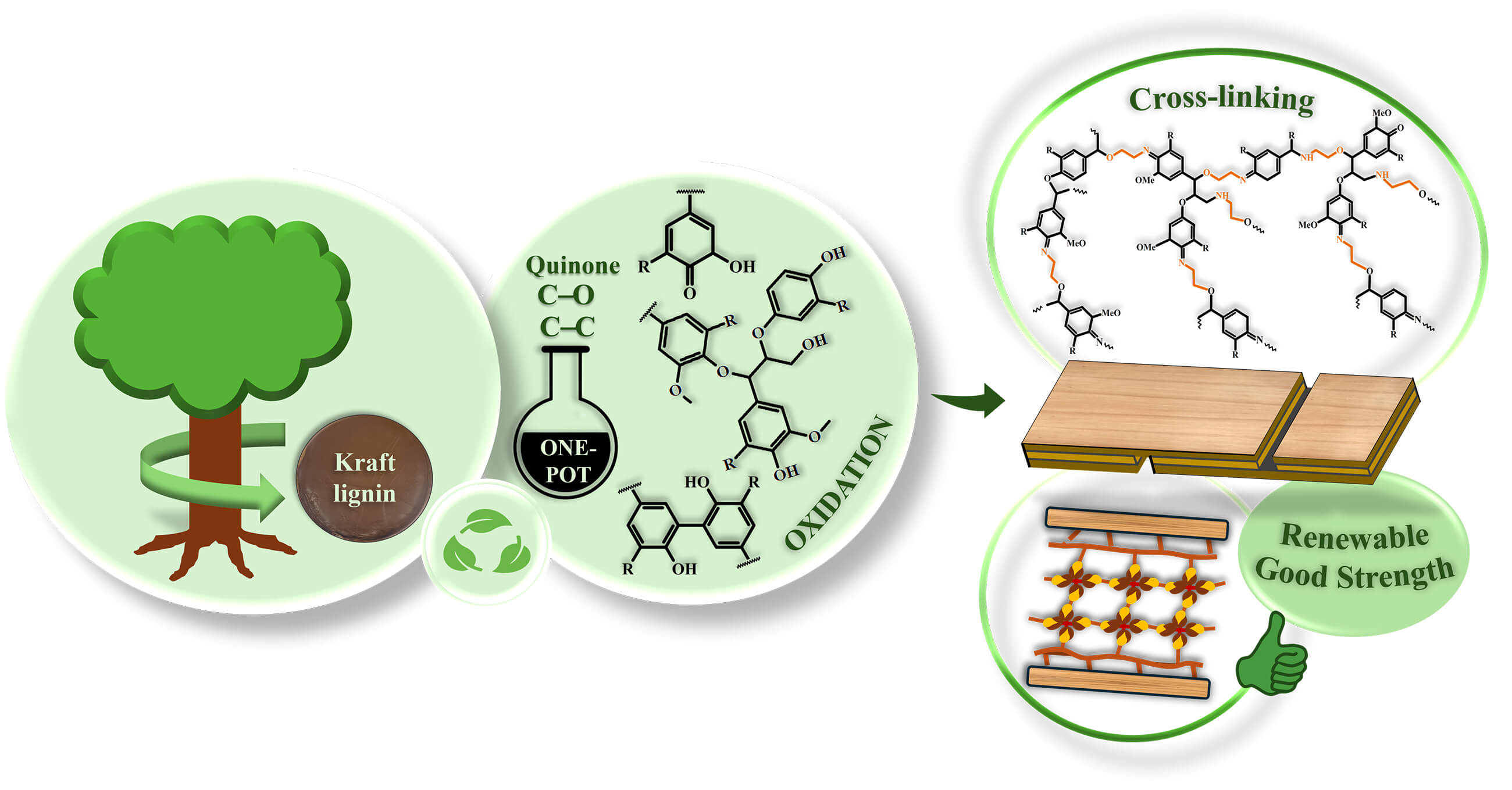
Abstract As the most abundant aromatic bio-based polymer, lignin has great potential as a sustainable feedstock for building crosslinked thermoset polymers as bio-based adhesives. However, the potential of hardwood kraft lignin (HKL) is limited due to its poor crosslinking reactivity. Hence, for the first time, the present study reports the facile oxidation of HKL involving a redox reaction with silver-ammonia complexes ([(AgNH3)2]+), primarily focusing on oxidation to produce reactive quinones and promote C–C linkages during reaction. This study aims to increases reactivity of oxidized HKL for effective crosslinking with monoethanolamine (MEA) for the development of bio-based wood… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tarek Dayyoub1,2,*, Mikhail Zadorozhnyy1,2, Dmitriy G. Ladokhin1, Emil Askerov1, Ksenia V. Filippova1, Lidiia D. Iudina1, Elizaveta Iushina1, Dmitry V. Telyshev1,3, Aleksey Maksimkin1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0022
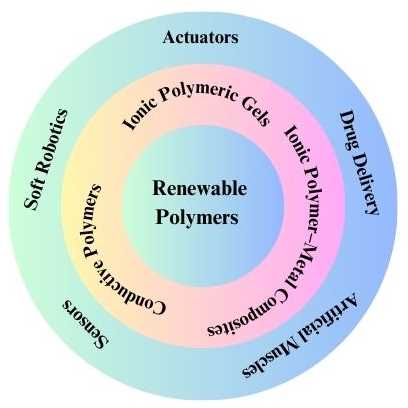
Abstract The development of actuators based on ionic polymers as soft robotics, artificial muscles, and sensors is currently considered one of the most urgent topics. They are lightweight materials, in addition to their high efficiency, and they can be controlled by a low power source. Nevertheless, the most popular ionic polymers are derived from fossil-based resources. Hence, it is now deemed crucial to produce these actuators using sustainable materials. In this review, the use of ionic polymeric materials as actuators is reviewed through the emphasis on their role in the domain of renewable materials. The review… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Irina Postnova1,2, Valeria Kurilenko3, Yury Shchipunov1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0032
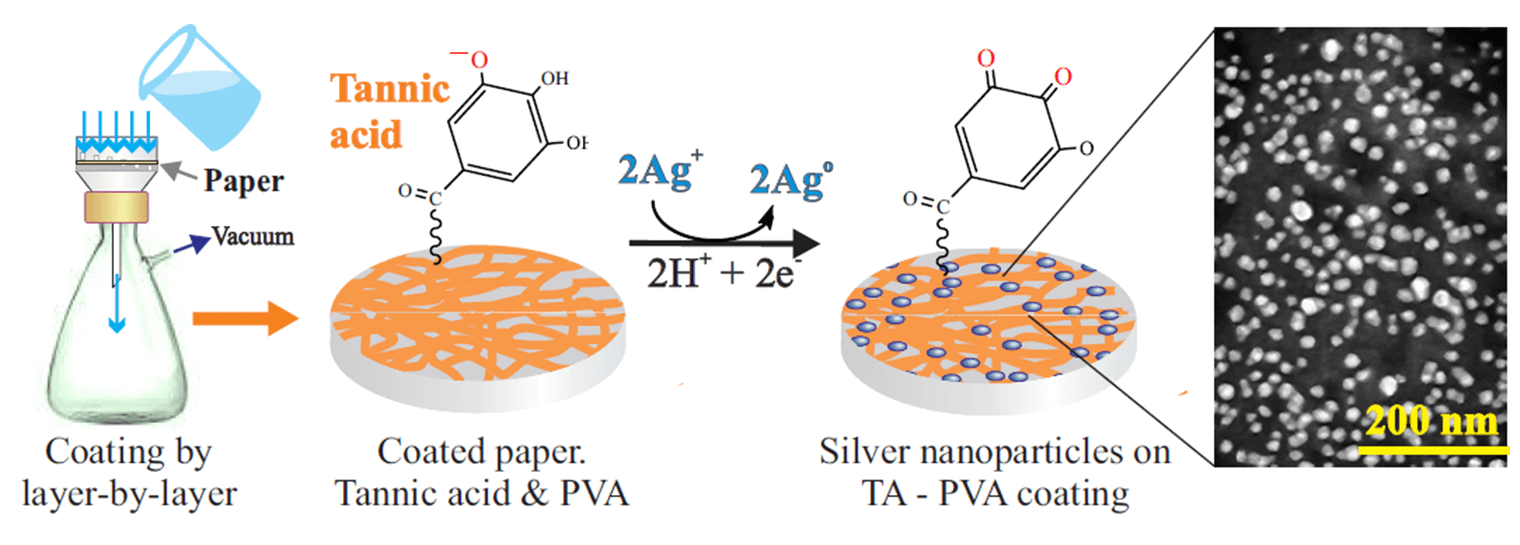
Abstract The main objective of the study was to prepare a highly active antimicrobial remedy by combining active agents such as tannic acid and silver nanoparticles, which are usually used separately. This was achieved by applying a coating of 11 alternating layers of an insoluble complex of tannic acid with polyvinyl alcohol on paper by the layer-by-layer approach, on the surface of which uniformly distributed spherical silver nanoparticles of uniform size, mainly 20–30 nm, were synthesized by in situ reduction using tannic acid, which also acts as a stabilizer, or an external reducing agent, which prevented polyphenol More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Vahideh Pourghasemi-Soufiani1, Farid Amidi-Fazli1,2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0009
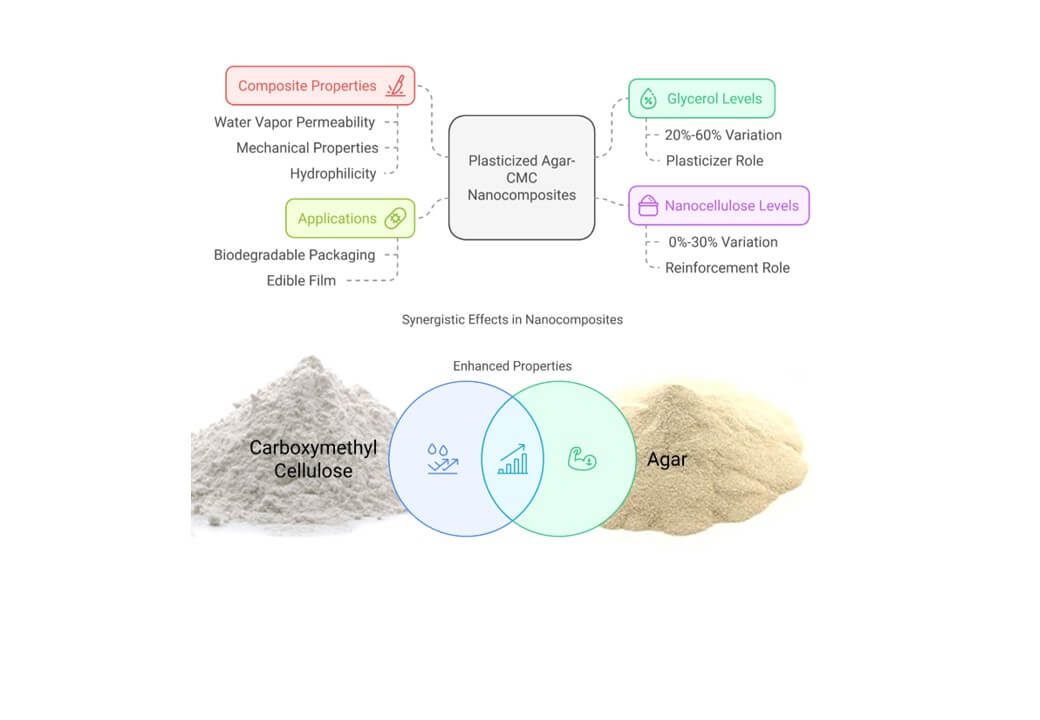
Abstract Biodegradable packaging has emerged as a viable alternative to non-biodegradable polymers. This study explores different treatments of agar-carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) nanocomposites developed via the casting method. We investigated the effects of varying glycerol levels (20%–60%) as a plasticizer and nanocellulose levels (0%–30%) as a filler on the properties of agar-CMC nanocomposites. Key properties analyzed included water vapor permeability, solubility in water, moisture absorption, water contact angle, color properties, and mechanical properties. The films exhibited low water vapor permeability, ranging from 2.50 × 10−11 g/msPa to 2.23 × 10−12 g/msPa. Water solubility of the films was below… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenny Surya Murtius1,2,*, Bambang Dwi Argo3,*, Irnia Nurika1, Sukardi1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0004
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Special issue from 1st International Conference of Natural Fiber and Biocomposite (1st ICONFIB) 2024 )
Abstract A stepwise pretreatment process for coconut dregs (CD) has been investigated to enhance availability of hemicellulose. Recently, lignocellulose-rich agricultural waste such as CD has garnered substantial attention as a sustainable raw material for producing value-added bio-products. To optimize the process variables within the stepwise pretreatment using Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) and Solid-State Fermentation (SSF), Response Surface Methodology (RSM) based on Central Composite Design (CCD) was employed. PEF, a non-thermal physical treatment, offers advantages such as low energy consumption and reduced processing times, while SSF utilizes Pleurotus ostreatus to promote biodegradation. A statistical model was constructed using… More >
Graphic Abstract
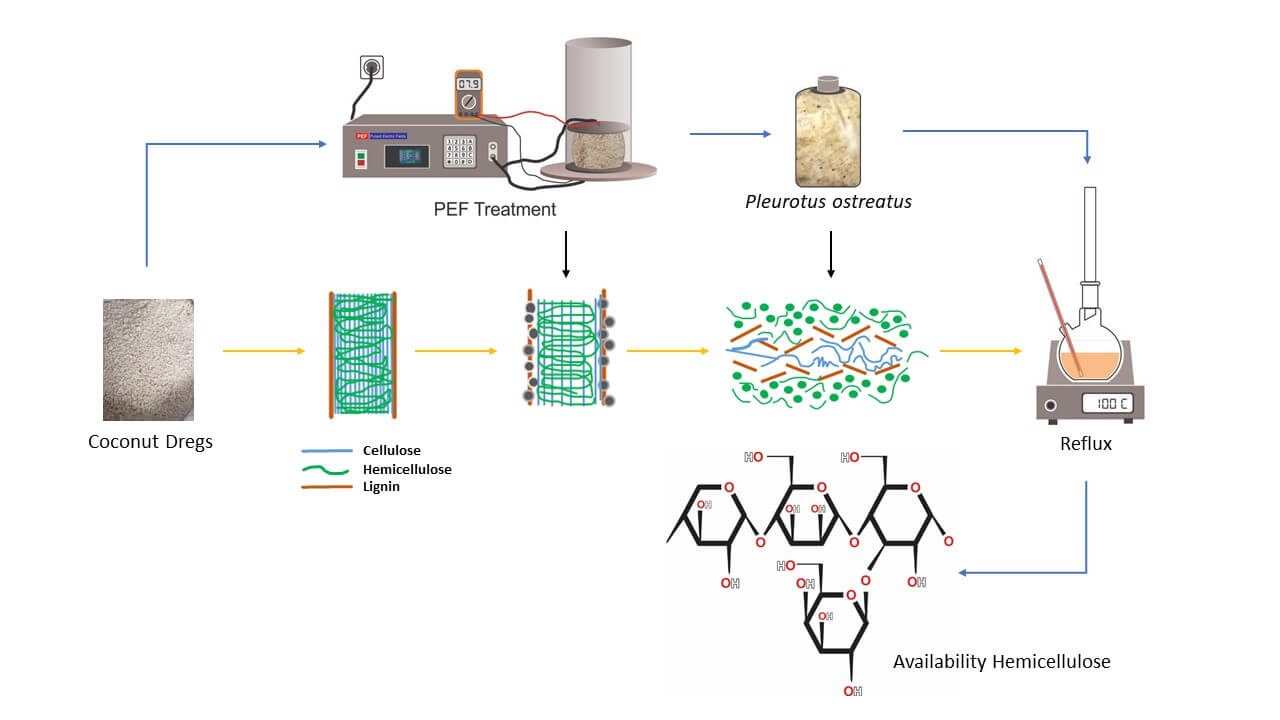
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Panji Setya Utama Putra1, Damar Rastri Adhika2,3,*, Lia Amelia Tresna Wulan Asri4, Suprijadi Suprijadi3,5
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0002
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Special issue from 1st International Conference of Natural Fiber and Biocomposite (1st ICONFIB) 2024 )
Abstract The continuous increase in petroleum-based plastic food packaging has led to numerous environmental concerns. One effort to reduce the use of plastic packaging in food is through preservation using biopolymer-based packaging. Among the many types of biopolymers, chitosan is widely used and researched due to its non-toxic, antimicrobial, and antifungal properties. Chitosan is widely available since it is a compound extracted from seafood waste, especially shrimps and crabs. The biodegradability and biocompatibility of chitosan also showed good potential for various applications. These characteristics and properties make chitosan an attractive biopolymer to be implemented as food… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Eko Budi Santoso1,2, Nur Izyan Wan Azelee3,4, Deded Sarip Nawawi2, Wasrin Syafii2,*, Widya Fatriasari2,5,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.058804
Abstract The significant amount of ash content in agricultural biomass presents an enormous challenge for efficient conversion processes. In addressing this issue, various deashing treatments have been tested and established, including simple leaching techniques, which can either be performed with or without the addition of chemical agents. These techniques hold promise for improving the deashing efficiency while potentially altering the structural and chemical composition of biomass, specifically lignin content, which is the key focus of this review. This review starts by exploring the presence of ash in agricultural residues and its impact on biomass properties. Next,… More >
Graphic Abstract
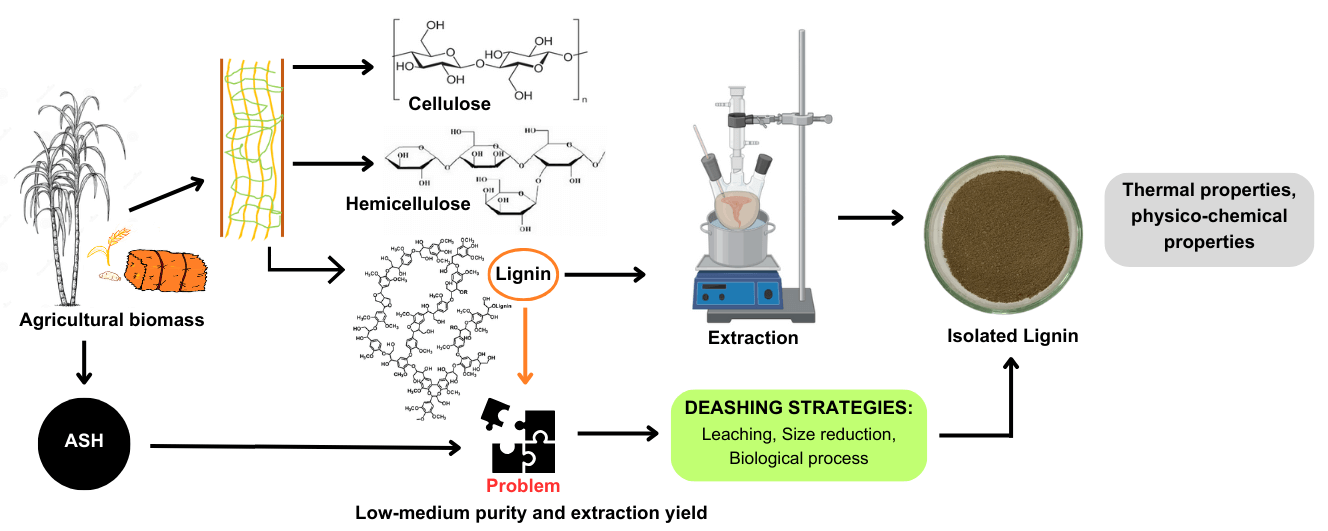
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enas Hassan1, Wafaa Abou-Elseoud1,2, Samar El-Mekkawi3, Mohammad Hassan1,2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0030
Abstract Saccharification of lignocellulosic wastes is the bottleneck of different bio-based chemical industries. Using enzymes for saccharification of lignocellulosic materials has several advantages over using chemicals. In the current work, the application of the Maximyze® enzyme system, which is industrially used in papermaking, was investigated in the saccharification of paper sludge and fiber dust wastes from the tissue paper industry. For optimizing the saccharification process, the effects of the consistency %, enzyme loading, and incubation time were studied and optimized using the Response Surface Methodology. The effect of these factors on the weight loss of paper… More >
Graphic Abstract
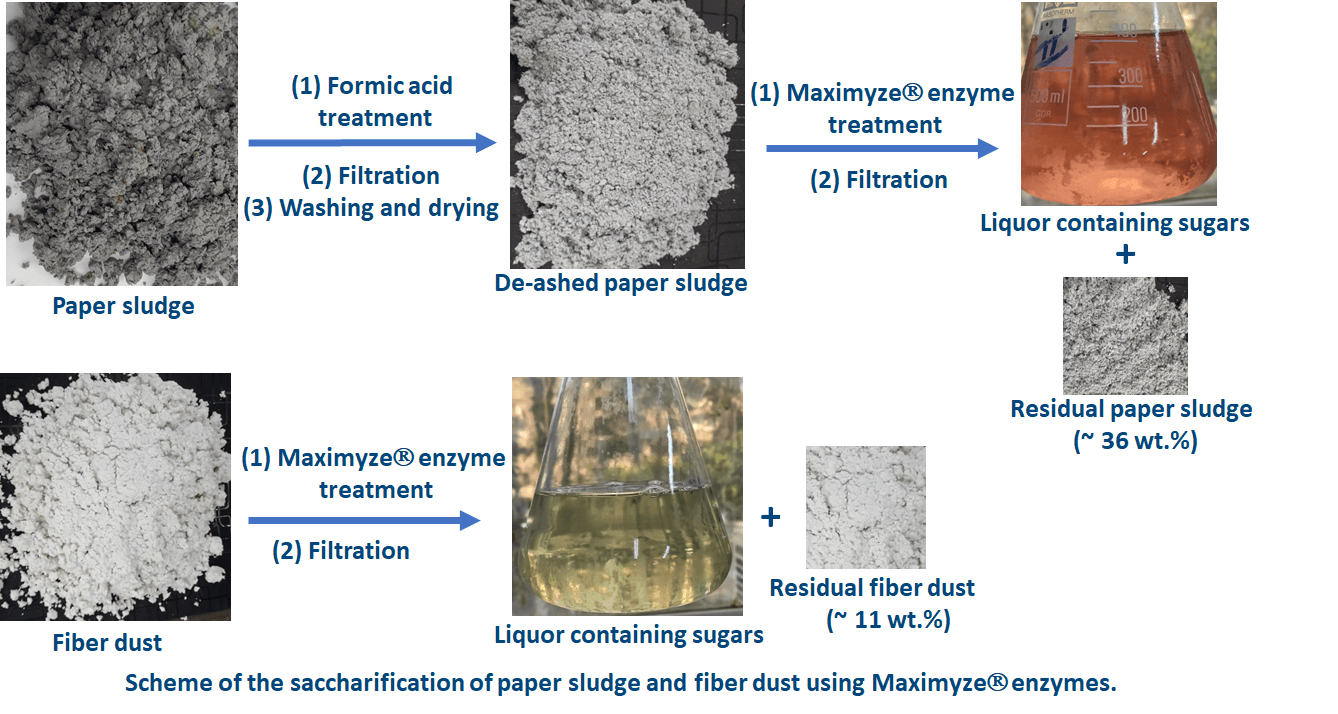
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohamed El-Sakhawy1,*, Sally A. Abdel-Halim2, Hebat-Allah S. Tohamy1, Hossam M. El-Masry3, Mona Mohamed AbdelMohsen2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0024
Abstract This study prepared and characterized amphiphilic carboxymethyl cellulose stearate (CMCS) recycled from sugarcane bagasse agro-waste (SB). The Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) analysis confirmed cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and CMCS structures, with CMCS showing increased H-bonding. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) revealed reduced crystallinity in CMC and CMCS. CMCS exhibited a hydrophobic nature but dispersed in water, enabling nanoemulsion formation. Optimal nanoemulsion was achieved with CMCS1, showing a particle size of 99 nm. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed CMC’s honeycomb structure, transforming into spherical particles in CMCS1. Antimicrobial tests demonstrated strong activity of CMCS formulations against Escherichia coli More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Flávia Naves Ferreira do Prado1, Michelle Garcia Gomes1, Marcela Piassi Bernardo1, Daniel Pasquini1,*, Anízio Márcio de Faria2, Luís Carlos de Morais3,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0014
Abstract Alternative methods for biodiesel purification that focus on ease of operation, cost reduction, and elimination of contaminated residues or that are easier to treat have received more attention. The dry wash route was used as an alternative to the wet route in biodiesel production. Filter membranes were developed based on cellulose nanofibers as the matrix and sugarcane bagasse fibers or soy hulls, as reinforcement to the matrix, before and after two chemical treatments (carboxymethylation and regeneration with sulfuric acid). The filters were characterized by permeability capacity, morphology, wettability, porosity, SEM and mechanical properties. The filtered… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
John Nwoanjia1, Jean Jalin Eyinga Biwôlé1,2,*, Joseph Zobo Mfomo1, Evariste Fedoung Fongnzossie1, Antonio Pizzi2, Salomé Ndjakomo Essiane3, Achille Bernard Biwole1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0005
Abstract This review aims to identify the assets and limitations of Dabema (Piptadeniastrum africanum) as a sustainable alternative to traditional timber species for furniture and construction applications. Dabema is characterized by its high density and dimensional stability, meeting ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards for mechanical strength, which is essential for promoting its use. However, its limited availability in trade and ingrained habits of use are obstacles to its widespread commercialization. In addition, thermal and oleothermal treatments have shown great potential for improving the characteristics of this wood, although they require ongoing optimization and rigorous More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
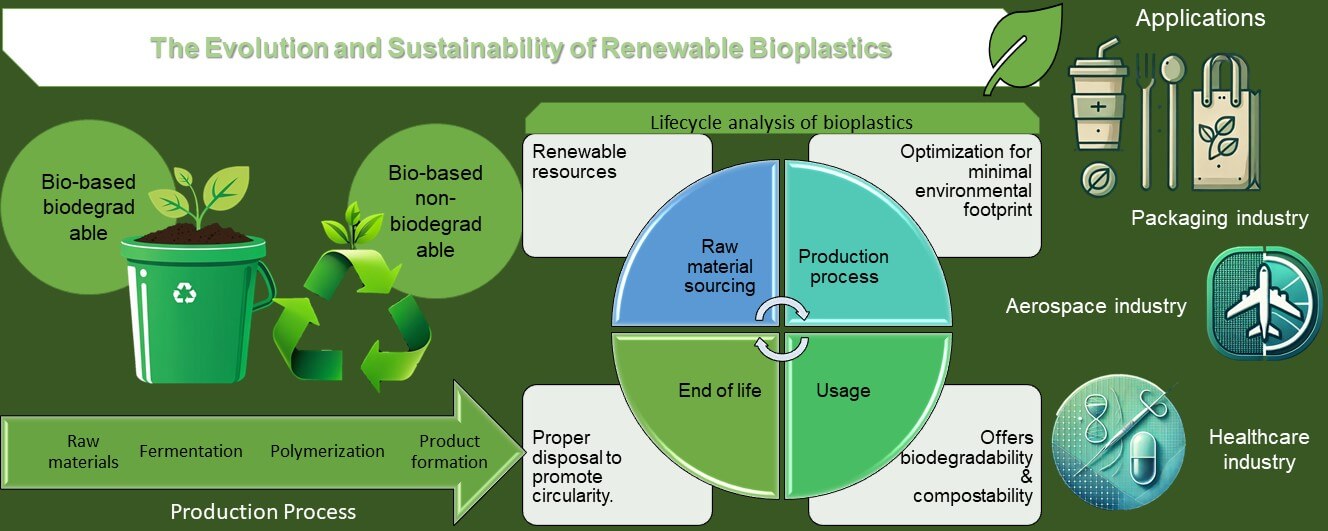
Farah Syazwani Shahar1, Thinesh Sharma Balakrishnan2, Mohamed Thariq Hameed Sultan2,3,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2024.02024-0011
Abstract In this comprehensive review, the evolution and progress of bioplastics are examined, with an emphasis on their types, production methods, environmental impact, and biodegradability. In light of the increasing global efforts to address environmental degradation, bioplastics have emerged as a highly potential substitute for conventional petroleum-based plastics. This review classifies various categories of bioplastics, encompassing both biodegradable and bio-based variations, and assesses their environmental consequences using life cycle evaluations and biodegradability calculations. This paper analyzes the technological advancements that have enhanced the mechanical and thermal characteristics of bioplastics, hence increasing their feasibility for extensive commercial… More >
Graphic Abstract