 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
David He1,*, Miao He2, Jay Yoon3
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063975
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applications of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Prognostics and Health Management)
Abstract Full ceramic bearings are mission-critical components in oil-free environments, such as food processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and medical applications. Developing effective fault diagnosis methods for these bearings is essential to ensuring operational reliability and preventing costly failures. Traditional supervised deep learning approaches have demonstrated promise in fault detection, but their dependence on large labeled datasets poses significant challenges in industrial settings where fault-labeled data is scarce. This paper introduces a few-shot learning approach for full ceramic bearing fault diagnosis by leveraging the pre-trained GPT-2 model. Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-2, pre-trained on diverse textual data,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yi-Chen Lee1, Yann-Horng Lin2, Wen-Jer Chang2,*, Muhammad Shamrooz Aslam3,*, Zi-Yao Lin2
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064717
Abstract An optimal fuzzy tracking synthesis for nonlinear discrete-time descriptor systems is discussed through the Parallel Distributed Compensation (PDC) approach and the Proportional-Difference (P-D) feedback framework. Based on the Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Descriptor Model (T-SFDM), a nonlinear discrete-time descriptor system is represented as several linear fuzzy subsystems, which facilitates the linear P-D feedback technique and streamlines the fuzzy controller design process. Leveraging the P-D feedback fuzzy controller, the closed-loop T-SFDM can be transformed into a standard system that guarantees non-impulsiveness and causality for the nonlinear discrete-time descriptor system. In view of the disturbance problems, a passive performance… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Muhammad Asif Zahoor Raja1, Aqsa Zafar Abbasi2, Kottakkaran Sooppy Nisar3,*, Ayesha Rafiq2, Muhammad Shoaib4
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.058020
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Developments on Computational Biology-II)
Abstract Being a nonlinear operator, fractional derivatives can affect the enforcement of existence at any given time. As a result, the memory effect has an impact on all nonlinear processes modeled by fractional order differential equations (FODEs). The goal of this study is to increase the fractional model of the TB virus’s (FMTBV) accuracy. Stochastic solvers have never been used to solve FMTBV previously. The Bayesian regularized artificial (BRA) method and neural networks (NNs), often referred to as BRA-NNs, were used to solve the FMTBV model. Each scenario features five occurrences that each reflect a different… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lord Amoah1,2, Jinwei Wang1,2,3,*, Bernard-Marie Onzo1,2
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063992
Abstract Medical image segmentation, i.e., labeling structures of interest in medical images, is crucial for disease diagnosis and treatment in radiology. In reversible data hiding in medical images (RDHMI), segmentation consists of only two regions: the focal and nonfocal regions. The focal region mainly contains information for diagnosis, while the nonfocal region serves as the monochrome background. The current traditional segmentation methods utilized in RDHMI are inaccurate for complex medical images, and manual segmentation is time-consuming, poorly reproducible, and operator-dependent. Implementing state-of-the-art deep learning (DL) models will facilitate key benefits, but the lack of domain-specific labels… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tallha Akram1,*, Fahdah Almarshad1, Anas Alsuhaibani1, Syed Rameez Naqvi2,3
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064079
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, with an increasing incidence over recent years. Over the past decade, researchers have recognized the potential of computer vision algorithms to aid in the early diagnosis of melanoma. As a result, a number of works have been dedicated to developing efficient machine learning models for its accurate classification; still, there remains a large window for improvement necessitating further research efforts. Limitations of the existing methods include lower accuracy and high computational complexity, which may be addressed by identifying and selecting the most discriminative features to improve classification… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Muhammad Sarwar1,2,*, Rafiq Alam1, Kamaleldin Abodayeh2,*, Saowaluck Chasreechai3,4, Thanin Sitthiwirattham4,5
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.062139
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Ambient Intelligence and Social Computing under uncertainty and indeterminacy: From Theory to Applications)
Abstract In this manuscript, the notion of a hesitant fuzzy soft fixed point is introduced. Using this notion and the concept of Suzuki-type (μ, ν)-weak contraction for hesitant fuzzy soft set valued-mapping, some fixed point results are established in the framework of metric spaces. Based on the presented work, some examples reflecting decision-making problems related to real life are also solved. The suggested method’s flexibility and efficacy compared to conventional techniques are demonstrated in decision-making situations involving uncertainty, such as choosing the best options in multi-criteria settings. We noted that the presented work combines and generalizes two More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fatima Asiri*, Wajdan Al Malwi
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064348
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Technologies in Information Security )
Abstract Ensuring information security in the quantum era is a growing challenge due to advancements in cryptographic attacks and the emergence of quantum computing. To address these concerns, this paper presents the mathematical and computer modeling of a novel two-dimensional (2D) chaotic system for secure key generation in quantum image encryption (QIE). The proposed map employs trigonometric perturbations in conjunction with rational-saturation functions and hence, named as Trigonometric-Rational-Saturation (TRS) map. Through rigorous mathematical analysis and computational simulations, the map is extensively evaluated for bifurcation behaviour, chaotic trajectories, and Lyapunov exponents. The security evaluation validates the map’s… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Murad Khan1,*, Mohammed Faisal1, Fahad R. Albogamy2, Muhammad Diyan3
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063764
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Technologies in Information Security )
Abstract The rapid advancements in distributed generation technologies, the widespread adoption of distributed energy resources, and the integration of 5G technology have spurred sharing economy businesses within the electricity sector. Revolutionary technologies such as blockchain, 5G connectivity, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices have facilitated peer-to-peer distribution and real-time response to fluctuations in supply and demand. Nevertheless, sharing electricity within a smart community presents numerous challenges, including intricate design considerations, equitable allocation, and accurate forecasting due to the lack of well-organized temporal parameters. To address these challenges, this proposed system is focused on sharing extra electricity… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rajendran Thanikachalam1, Anandhavalli Muniasamy2, Ashwag Alasmari3, Rajendran Thavasimuthu4,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063063
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in AI-Driven Computational Modeling for Image Processing)
Abstract Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) and image mining are becoming more important study fields in computer vision due to their wide range of applications in healthcare, security, and various domains. The image retrieval system mainly relies on the efficiency and accuracy of the classification models. This research addresses the challenge of enhancing the image retrieval system by developing a novel approach, EfficientNet-Convolutional Neural Network (EffNet-CNN). The key objective of this research is to evaluate the proposed EffNet-CNN model’s performance in image classification, image mining, and CBIR. The novelty of the proposed EffNet-CNN model includes the integration… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yongli Liu1,2, Weihao Li1,2,*, Haitao Wang1,2,3, Taoren Du4
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064179
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning for Time Series Forecasting: Research and Applications)
Abstract Coal dust explosions are severe safety accidents in coal mine production, posing significant threats to life
and property. Predicting the maximum explosion pressure (Pm) of coal dust using deep learning models can effectively
assess potential risks and provide a scientific basis for preventing coal dust explosions. In this study, a 20-L explosion
sphere apparatus was used to test the maximum explosion pressure of coal dust under seven different particle sizes
and ten mass concentrations (Cdust), resulting in a dataset of 70 experimental groups. Through Spearman correlation
analysis and random forest feature selection methods, particle size (D10, D20, D50)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohsen Ali Alawami1, Dahyun Jung2, Yewon Park2, Yoonseo Ku2, Gyeonghwan Choi2, Ki-Woong Park2,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063819
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cutting-Edge Security and Privacy Solutions for Next-Generation Intelligent Mobile Internet Technologies and Applications)
Abstract To date, many previous studies have been proposed for driver authentication; however, these solutions have many shortcomings and are still far from practical for real-world applications. In this paper, we tackle the shortcomings of the existing solutions and reach toward proposing a lightweight and practical authentication system, dubbed DriveMe, for identifying drivers on cars. Our novelty aspects are ① Lightweight scheme that depends only on a single sensor data (i.e., pressure readings) attached to the driver’s seat and belt. ② Practical evaluation in which one-class authentication models are trained from only the owner users and tested using… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qingyu Tan, Yan Li, Byeong-Seok Shin*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063811
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine learning and Blockchain for AIoT: Robustness, Privacy, Trust and Security)
Abstract Federated Learning (FL), a practical solution that leverages distributed data across devices without the need for centralized data storage, which enables multiple participants to jointly train models while preserving data privacy and avoiding direct data sharing. Despite its privacy-preserving advantages, FL remains vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where malicious participants introduce backdoors into local models that are then propagated to the global model through the aggregation process. While existing differential privacy defenses have demonstrated effectiveness against backdoor attacks in FL, they often incur a significant degradation in the performance of the aggregated models on benign tasks.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sirawit Makaew, Yupaporn Areepong*, Saowanit Sukparungsee
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063459
Abstract This study aims to examine the explicit solution for calculating the Average Run Length (ARL) on the triple exponentially weighted moving average (TEWMA) control chart applied to autoregressive model (AR(p)), where AR(p) is an autoregressive model of order p, representing a time series with dependencies on its p previous values. Additionally, the study evaluates the accuracy of both explicit and numerical integral equation (NIE) solutions for AR(p) using the TEWMA control chart, focusing on the absolute percentage relative error. The results indicate that the explicit and approximate solutions are in close agreement. Furthermore, the study More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuanzhuo Wang, Honghua Dai*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064416
Abstract To establish the optimal reference trajectory for a near-space vehicle under free terminal time, a time-optimal model predictive static programming method is proposed with adaptive fish swarm optimization. First, the model predictive static programming method is developed by incorporating neighboring terms and trust region, enabling rapid generation of precise optimal solutions. Next, an adaptive fish swarm optimization technique is employed to identify a sub-optimal solution, while a momentum gradient descent method with learning rate decay ensures the convergence to the global optimal solution. To validate the feasibility and accuracy of the proposed method, a near-space More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kachi Anvesh1,2, Bharati M. Reshmi2,3, Shanmugasundaram Hariharan4, H. Venkateshwara Reddy5, Murugaperumal Krishnamoorthy6, Vinay Kukreja7, Shih-Yu Chen8,9,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063239
Abstract Automated classification of retinal fundus images is essential for identifying eye diseases, though there is earlier research on applying deep learning models designed especially for detecting tessellation in retinal fundus images. This study classifies 4 classes of retinal fundus images with 3 diseased fundus images and 1 normal fundus image, by creating a refined VGG16 model to categorize fundus pictures into tessellated, normal, myopia, and choroidal neovascularization groups. The approach utilizes a VGG16 architecture that has been altered with unique fully connected layers and regularization using dropouts, along with data augmentation techniques (rotation, flip, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sangmin Kim1, Byeongcheon Lee1, Muazzam Maqsood2, Jihoon Moon3,*, Seungmin Rho4,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.061653
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Technologies and Applications)
Abstract The increased accessibility of social networking services (SNSs) has facilitated communication and information sharing among users. However, it has also heightened concerns about digital safety, particularly for children and adolescents who are increasingly exposed to online grooming crimes. Early and accurate identification of grooming conversations is crucial in preventing long-term harm to victims. However, research on grooming detection in South Korea remains limited, as existing models trained primarily on English text and fail to reflect the unique linguistic features of SNS conversations, leading to inaccurate classifications. To address these issues, this study proposes a novel… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiming Zhou1, Jinhua Zhang2,3, Kai Long2,*, Ayesha Saeed2, Yutang Chen2, Rongrong Geng2, Tao Tao4, Xiaohui Guo1
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063034
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Engineering Applications)
Abstract The jacket structure and transition piece comprise the supporting structure of a bottom-fixed offshore
wind turbine (OWT) connected to the steel tower, which determines the overall structural dynamic performance of the
entire OWT. Ideally, optimal performance can be realized by effectively coordinating two components, notwithstanding
their separate design processes. In pursuit of this objective, this paper proposes a concurrent design methodology
for the jacket structure and transition piece by exploiting topology optimization (TO). The TO for a three-legged
jacket foundation is formulated by minimizing static compliance. In contrast to conventional TO, two separated
volume fractions… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chiara Innocente1,*, Matteo Boemio2, Gianmarco Lorenzetti2, Ilaria Pulito2, Diego Romagnoli2, Valeria Saponaro2, Giorgia Marullo1, Luca Ulrich1, Enrico Vezzetti1
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063186
Abstract Lip-reading technology, based on visual speech decoding and automatic speech recognition, offers a promising solution to overcoming communication barriers, particularly for individuals with temporary or permanent speech impairments. However, most Visual Speech Recognition (VSR) research has primarily focused on the English language and general-purpose applications, limiting its practical applicability in medical and rehabilitative settings. This study introduces the first Deep Learning (DL) based lip-reading system for the Italian language designed to assist individuals with vocal cord pathologies in daily interactions, facilitating communication for patients recovering from vocal cord surgeries, whether temporarily or permanently impaired. To… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ashish Rayal1, Priya Dogra1, Sabri T. M. Thabet2,3,4,*, Imed Kedim5, Miguel Vivas-Cortez6,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.060989
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Analytical and Numerical Solution of the Fractional Differential Equation)
Abstract The Rössler attractor model is an important model that provides valuable insights into the behavior of chaotic systems in real life and is applicable in understanding weather patterns, biological systems, and secure communications. So, this work aims to present the numerical performances of the nonlinear fractional Rössler attractor system under Caputo derivatives by designing the numerical framework based on Ultraspherical wavelets. The Caputo fractional Rössler attractor model is simulated into two categories, (i) Asymmetric and (ii) Symmetric. The Ultraspherical wavelets basis with suitable collocation grids is implemented for comprehensive error analysis in the solutions of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wencheng Wang1,2,*, Baoxin Yin1,2, Lei Li2,*, Lun Li1, Hongtao Liu1
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063595
Abstract In low-light environments, captured images often exhibit issues such as insufficient clarity and detail loss, which significantly degrade the accuracy of subsequent target recognition tasks. To tackle these challenges, this study presents a novel low-light image enhancement algorithm that leverages virtual hazy image generation through dehazing models based on statistical analysis. The proposed algorithm initiates the enhancement process by transforming the low-light image into a virtual hazy image, followed by image segmentation using a quadtree method. To improve the accuracy and robustness of atmospheric light estimation, the algorithm incorporates a genetic algorithm to optimize the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Umit Cigdem Turhal1, Yasemin Onal1,*, Kutalmis Turhal2
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.064269
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods Applied to Energy Systems)
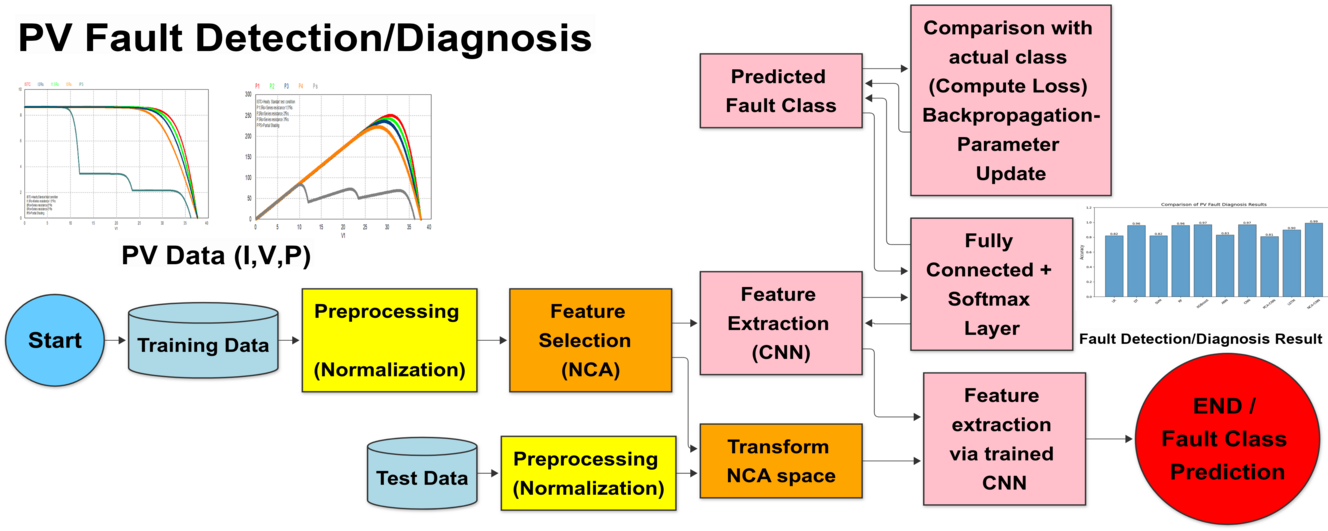
Abstract The reliability and efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) systems are essential for sustainable energy production, requiring accurate fault detection to minimize energy losses. This study proposes a hybrid model integrating Neighborhood Components Analysis (NCA) with a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to improve fault detection and diagnosis. Unlike Principal Component Analysis (PCA), which may compromise class relationships during feature extraction, NCA preserves these relationships, enhancing classification performance. The hybrid model combines NCA with CNN, a fundamental deep learning architecture, to enhance fault detection and diagnosis capabilities. The performance of the proposed NCA-CNN model was evaluated against other More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gebrail Bekdaş1, Yaren Aydın1, Celal Cakiroglu2, Umit Işıkdağ3,*
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.063909
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Frontiers in Computational Modeling and Simulation of Concrete)
Abstract Retaining walls are utilized to support the earth and prevent the soil from spreading with natural slope angles where there are differences in the elevation of ground surfaces. As the need for retaining structures increases, the use of retaining walls is increasing. The retaining walls, which increase the stability of levels, are economical and meet existing adverse conditions. A considerable amount of retaining walls is made from steel-reinforced concrete. The construction of reinforced concrete retaining walls can be costly due to its components. For this reason, the optimum cost should be targeted in the design… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Smita Mahajan1, Shilpa Gite1,2, Biswajeet Pradhan3,*, Abdullah Alamri4, Shaunak Inamdar5, Deva Shriyansh5, Akshat Ashish Shah5, Shruti Agarwal5
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.058456
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in AI-Driven Computational Modeling for Image Processing)
Abstract The development of generative architectures has resulted in numerous novel deep-learning models that generate images using text inputs. However, humans naturally use speech for visualization prompts. Therefore, this paper proposes an architecture that integrates speech prompts as input to image-generation Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) model, leveraging Speech-to-Text translation along with the CLIP + VQGAN model. The proposed method involves translating speech prompts into text, which is then used by the Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) + Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network (VQGAN) model to generate images. This paper outlines the steps required to implement such a… More >